Describe the Normal Distribution of Water in the Body
Interstitial fluid contains 25 of the total body water. Cell life - distribute nutrients to cells ie.

Distribution Of Total Body Water Tbw Within The Body Showing The Download Scientific Diagram
The intracellular fluid compartment contains most of the water in the body 67 of total.

. The bodys fluid separates into two main compartments. The percentage of body weight that is water is also lower in older people and in. Water makes up 50 to 70 per cent of the weight of the adult human body and varies inversely as the fat content.
This mentioned amount of water is distributed throughout the body as the major component of the. Describe the normal distribution of water in the body a. Chemical and metabolic reactions - removal of waste products toxins from the organs.
For a complete diagram of body fluid compartments see body fluid. Generally the water content of the grey matter was higher than that of the white matter and increased from the frontal to the occipital and from the parietal to the basal cortex. The intracellular fluid comprises about 23 rd of water and the remaining 13 rd of water is present in the extracellular fluid.
This is because women typically have less skeletal muscle and more fat than males. The cell membrane actually provides the boundary in between the extracellular and the intracellular compartments. In contrast skeletal muscle contains 75 water.
Water accounts for about one half to two thirds of an average persons weight. Humans are approximately 75 water by mass as infants and 50 to 60 water by mass as adults. Textbook solution for Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy Physiology 13th Edition David N.
Water Balance and ECF Osmolality. It is also used to facilitate all the previously mentioned functions in the body. Water leaves the body through several routes - the evaporation of sweat in the moisture of exhaled breath in the urine and in the faeces.
Extreme values in both tails of the distribution are similarly unlikely. This amounts equals between 14-28 litres per day. We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts.
Extracellular fluid includes interstitial fluid plasma lymph and transcellular fluid. Describe the normal distribution of water in the body. Body content of water or electrolytes rises if intake exceeds outflow.
Distribution of water within the body. Urine 60 Feces 4. All of the water and electrolytes enclosed by cell membranes constitute the.
Furthermore fluid is always in flux through a variety of regulatory. Transport of nutrients participates in the breakdown of food. Total body water as of BODY WEIGHT ICF 40 ECF 20.
Our body contains water distributed in two compartments namely intracellular and extracellular compartments. Introduction The normal body in an average adult male is composed of water 60 minerals 7 protein and related substances 18 fat 15 The water denoted by the term total body water TBW the electrolytes need special emphasis TBW 10 lower in young females In infants TBW is 65-75 of body weight 4. Water intake sources Ingested fluid 60 and solid food 30 Metabolic water or water of oxidation 10 Water Output.
Vitamins minerals and glucose. Intracellular fluid volume ICFV and extracellular fluid volume ECFV. Fat is relatively free of water -- TBWWeight ratio changes with fat Ratio is lower in woman and decrease with age.
The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that is symmetrical around its mean most of the observations cluster around the central peak and the probabilities for values further away from the mean taper off equally in both directions. Fat tissue has a lower percentage of water than lean tissue and women tend to have more fat so the percentage of body weight that is water in the average woman is lower 52 to 55 than it is in the average man 60. The amount of water that surrounds our cells accounts for 13 of our TBW.
To remain properly hydrated water intake must equal water output. First week only 499. Start your trial now.
The distribution of body water in different compartments has been presented schematically in Fig. Protein 18 Mineral 7 Fat 15 Water 60. Distribution of Body Fluids 212 numbers 2 3 4 2.
Most of the water about 63 is intracellular the remainder about 37 is extracellular. Explain how the fluids in the compartments different in composition. Fluid Concentration in Human Body.
Water content of LEAN body tissues is constant 71-72mL100g. Extracellular fluids generally have similar compositions including relatively high concentrations of sodium chloride and bicarbonate ions and lesser. The average young man is around 60 water while a healthy young woman is about 50.
The water of the body can be considered to be distributed within two main compartmentsthe extracellular and the intracellular. The amount of water thats inside our cells accounts for 23rds of our TBW. Adipose fat tissue is the least hydrated tissue in the body 20 hydrated even bone contains more water than fat.
Solution for Describe the normal distribution of water in the body. Human beings are creatures that are primarily composed of water. Plasma is the smallest fluid compartment 8 of total body water.
Note that this diagram places focus only on these three major fluid compartments. 63 is housed in intracellular fluid compartments and 37 is. Our body contains water distributed in two compartments namely intracellular and extracellular compartments The intracellular fluid comprises about 23 rd of water and the remaining 13 rd of water is present in the extracellular fluid.
Water has five main functions in the body of which includes. Even adjacent cortical regions showed differences in the amount of brain water of up to 341. Distribution of body water in WG21.
Of the 42L of water found in the body two-thirds of it is within the intracellular fluid ICF space which equates to 28L. Describe the normal distribution of water in the body. ECF is also known as interstitial fluid because its the fluid in between the cells.
It is the essence of life and the aqueous base solution in which all essential biochemical processes occur that produce life. Chapter 182 Problem 2P. Weve got the study and writing resources you need for.

Body Fluids And Fluid Compartments Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Physiology Figure Body Fluid Compartments Of A 70 Kg Adult Man Physiologyweb

Body Fluids And Fluid Compartments Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Process Capability Analysis In Laboratory Quality Control Northwest Analytics Process Capability Analysis Change Management

Pin On Paleo Magazine Articles
The Normal Distribution Clearly Explained Youtube

Kidney Support Gold For Cat Kidney Function Natural Herbal Remedies Cat Kidney Fluid And Electrolytes

Distribution Of Body Water Physiology Body Weight Body

Body Fluids And Fluid Compartments Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Professional Pet Supplies Products Accessories And Equipment Online In 2022 Milk Thistle Liver Disease Healthy Liver
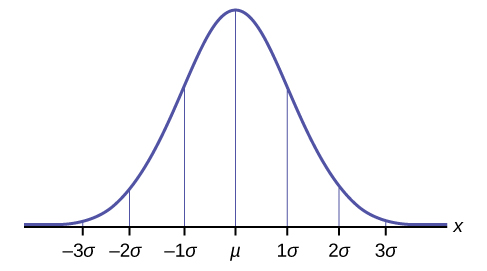
The Standard Normal Distribution Introductory Business Statistics

Distribution Of Water In The Body Fluid Compartments Youtube

Finding Areas Under And What Is The Standard Normal Distribution Curve And Z Scores Explained Youtube

Kinetic Energy Of A Rigid Body With Velocity In The Xy Plane Kinetic Energy Velocity Kinetic

Distribution Of Total Body Water Tbw Within The Body Showing The Download Scientific Diagram




Comments
Post a Comment